Best Physiotherapy in Ghaziabad – Trusted Care for Pain Relief & Recovery
Physiotherapy in Ghaziabad offers reliable and effective solutions for people suffering from back pain, neck pain, joint stiffness, sports injuries, and post-surgical recovery. Skilled physiotherapists focus on identifying the root cause of pain and designing personalized treatment plans using exercises, manual therapy, electrotherapy, and posture correction techniques. The goal is not only pain relief but also long-term recovery and improved mobility. With a patient-centric approach and modern rehabilitation methods, physiotherapy helps individuals regain strength, enhance flexibility, prevent future injuries, and return to an active, healthy lifestyle with confidence.
Providing excellent & expert therapy service according to need
Sports Massage Therapy

Chiropractic Therapy
Pedaitric Rehablitiaon

Cardio Rehabilitation
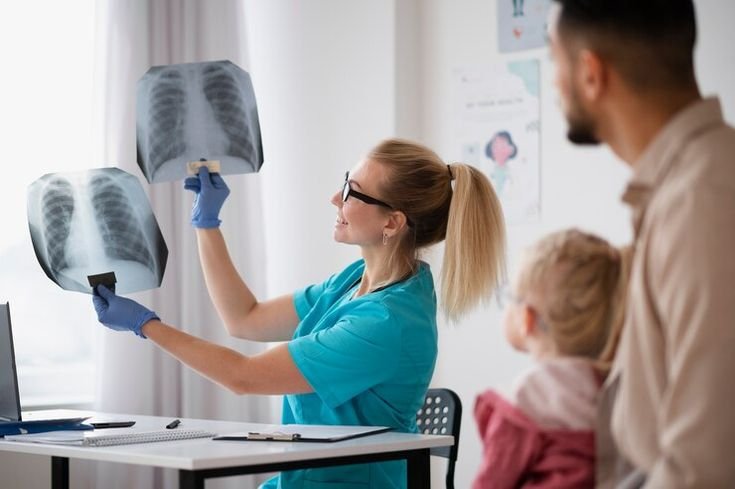
Respiratory rehabilitation

Following cutting-edge time-tested treatments to maximize quality of life
Offering advanced, proven physiotherapy treatments that promote healing, restore mobility, reduce pain, and enhance overall quality of life effectively.
Physiotherapy Service
At Austerities Physiotherapy, we provide advanced, personalized physiotherapy care to help you regain movement, reduce pain, and enhance your quality of life—all in the comfort of your home. Our services are tailored for individuals recovering from injuries, managing chronic conditions, or undergoing post-surgical rehabilitation.
Common Conditions We Treat:
- Back pain
- Neck pain
- Knee pain
- Frozen shoulder
- Arthritis
- Disc bulge and herniation
Post-Surgical Rehabilitation:
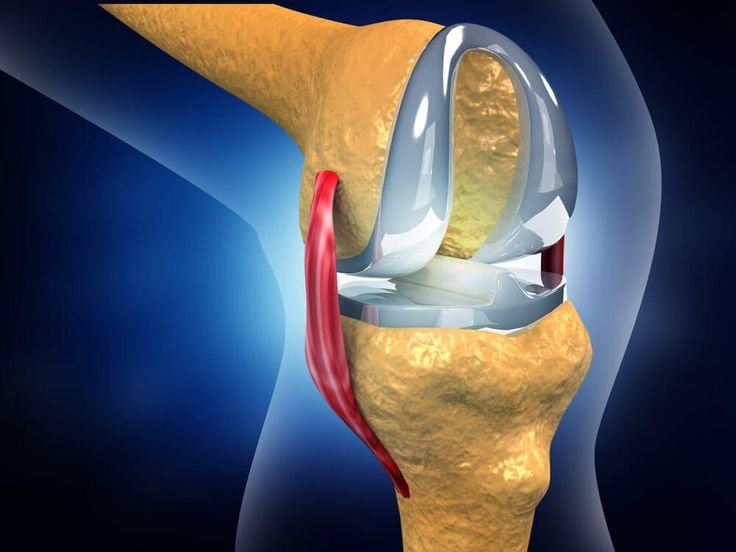
- Total Knee Replacement (TKR)
- Hip Replacement
- Ligament reconstruction
- Shoulder surgeries
Other Functional Issues:
- Muscle weakness
- Balance problems
- Muscle imbalance
- Age-related mobility loss
Symptoms We Address:
- Joint stiffness and inflammation
- Radiating or sharp pain
- Numbness or tingling sensations
- Difficulty walking or standing
- Facial drooping or muscle paralysis
- Loss of coordination and balance
- Tremors or uncontrolled movements
- Post-operative pain and limited mobility
Our highly trained physiotherapists at Austerities Physiotherapy work with patients of all age groups—from children to seniors—using evidence-based techniques to ensure fast, effective recovery. Each treatment plan is designed after a detailed assessment and is continually adapted based on patient progress.
Whether you’re dealing with a long-term condition or recovering from surgery, our goal is to help you move better, feel stronger, and live healthier. We bring hospital-quality care to your doorstep—with compassion, skill, and dedication.
Cerebral Palsy (CP) is a group of neurological disorders that affect movement, posture, and muscle coordination due to damage or abnormal development of the brain, typically before or during birth. Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in managing CP by improving motor skills, reducing muscle stiffness, enhancing balance, and encouraging independence in daily activities. The condition varies in severity from mild motor impairment to severe physical disability, and the symptoms can evolve as a child grows. With early intervention, physiotherapy can significantly improve functional outcomes, mobility, and quality of life for individuals with CP.
Common Conditions Treated in CP Physiotherapy:
- Spastic cerebral palsy (most common form with stiff muscles)
- Dyskinetic cerebral palsy (involuntary movements)
- Ataxic cerebral palsy (balance and coordination issues)
- Mixed type CP (combination of symptoms)
- Arthritis
- Muscle contractures and joint stiffness
- Poor motor control and coordination
- Delayed motor milestones (e.g., sitting, crawling, walking)
Post-Surgical Rehabilitation:
- Total Knee Replacement (TKR)
- Hip Replacement
- Ligament reconstruction
- Shoulder surgeries
Symptoms Managed through Physiotherapy:
- Muscle stiffness or spasticity
- Poor balance and coordination
- Difficulty with fine and gross motor skills
- Uncontrolled or jerky movements
- Floppiness (hypotonia) or exaggerated reflexes
- Uneven gait or limping
- Difficulty swallowing or speaking (in some cases)
- Postural issues (e.g., scoliosis, abnormal curvature)
- Contractures leading to restricted movement
- Delay in developmental milestones
- Limited ability to perform daily activities independently
Pre and post-surgical physiotherapy plays a crucial role in the recovery process for individuals undergoing various types of surgeries. Whether the surgery is orthopedic, neurological, or related to soft tissue injuries, physiotherapy can significantly impact healing, rehabilitation, and overall outcomes. In the pre-surgery phase, physiotherapy aims to prepare the body for surgery, reducing pain and improving mobility, while post-surgery physiotherapy focuses on recovery, minimizing complications, and restoring function.
Pre-Surgery Physiotherapy Conditions:
- Joint pain or stiffness: Patients with arthritis or joint problems can benefit from pre-surgery physiotherapy to improve flexibility and reduce pain.
- Muscle weakness: Strengthening exercises help enhance muscle stability, which is crucial for faster recovery after surgery.
- Poor posture and alignment: Pre-surgery treatment can correct postural imbalances, reducing the risk of complications during and after surgery.
- Limited range of motion: Pre-surgical physiotherapy helps increase the flexibility of joints and muscles before the surgery.
- Swelling and inflammation: Manual therapies and exercises can reduce swelling and prepare the body for surgery.
- Pre-existing conditions: Physiotherapy can optimize overall physical health, managing conditions like obesity, diabetes, or hypertension before surgery.contractures and joint stiffness
Post-Surgery Physiotherapy Conditions:
- Pain management: A key component in the initial stages after surgery, physiotherapists use techniques like TENS, massage, and heat/cold therapy to manage pain.
- Muscle weakness: Post-surgery, muscles can be weak due to disuse or immobilization, and physiotherapy aims to rebuild strength.
- Swelling and bruising: Therapeutic exercises and modalities can reduce post-surgical swelling and prevent complications.
- Scar tissue formation: Physiotherapy techniques like massage can help prevent the formation of excessive scar tissue that could limit mobility.
- Limited range of motion: Exercises and manual therapy are critical for restoring movement after surgery.
- Functional recovery: Physiotherapists focus on restoring independence and regaining daily functional activities, including walking, dressing, and cooking.
Post-Surgery Physiotherapy Symptoms Treated:
- Difficulty moving the operated body part
- Muscle weakness and stiffness
- Swelling around the surgery site
- Pain or discomfort during movement
- Fatigue or overall weakness post-surgery
In conclusion, pre and post-surgery physiotherapy plays an essential role in ensuring successful recovery. It helps to optimize mobility, reduce pain, prevent complications, and ultimately support patients in returning to their normal activities.
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder that primarily affects movement. It occurs due to the degeneration of dopamine-producing neurons in a specific area of the brain called the substantia nigra. Dopamine is a chemical messenger that plays a key role in sending signals to control smooth and coordinated muscle movements. As dopamine levels drop, individuals begin to experience motor and non-motor symptoms. Though it usually affects people above the age of 60, early-onset Parkinson’s can also occur. Physiotherapy plays a vital role in maintaining mobility, balance, and independence.
Conditions Associated with Parkinson’s Disease:
- Degeneration of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain
- Reduced dopamine levels affecting movement and coordination
- Progressive worsening of motor and cognitive functions
- Muscular rigidity and bradykinesia (slowness of movement)
- Balance and postural instability
Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease:
- Tremors: Involuntary shaking, especially at rest (commonly hands or fingers)
- Bradykinesia: Slowness of voluntary movement
- Muscle Rigidity: Stiffness in arms, legs, or trunk
- Postural Instability: Poor balance, risk of falls
- Shuffling Gait: Small, quick steps while walking
- Reduced Arm Swing: Decreased movement in arms while walking
Non-Motor Symptoms:
- Speech Changes: Soft or slurred speech
- Facial Masking: Reduced facial expressions
- Depression or Anxiety: Emotional disturbances
- Sleep Disorders: Insomnia or restless legs
- Constipation and urinary problems
Parkinson’s disease significantly impacts a person’s mobility and quality of life. Though it is a chronic and progressive condition, early diagnosis and comprehensive management can slow its progression. Physiotherapy is essential in improving muscle strength, balance, posture, and flexibility, thereby supporting individuals to live as independently and actively as possible.
Tennis elbow, medically known as lateral epicondylitis, is a condition that causes pain around the outside of the elbow. Despite its name, it can affect anyone—not just athletes—especially those who perform repetitive wrist and arm movements. It’s commonly seen in people who play racquet sports, but also in carpenters, painters, cooks, or office workers. The condition results from overuse of the forearm muscles and tendons, leading to small tears and inflammation around the elbow joint.
Conditions Related to Tennis Elbow:
- Overuse of wrist and forearm muscles
- Repetitive arm movements (e.g., playing tennis, typing, using tools)
- Poor ergonomics or improper technique
- Age-related degeneration (most common in adults aged 30–50)
Symptoms of Tennis Elbow:
Pain and Discomfort:
- Pain on the outer part of the elbow
- Discomfort that worsens with gripping, lifting, or twisting motions
- Pain radiating down the forearm
Weakness and Mobility Issues:
- Weak grip strength
- Difficulty lifting objects
- Stiffness in the elbow, especially in the morning
Functional Limitations:
- Trouble with basic tasks like turning a doorknob or
- Increased pain during activities like writing, typing, or brushing teeth shaking hands
Tennis elbow is a painful yet treatable condition caused by repetitive strain on the forearm muscles. It often starts gradually but can significantly impact daily activities if left unmanaged. Early physiotherapy interventions—such as rest, ice therapy, stretching, strengthening exercises, and ergonomic corrections—are essential for recovery. With proper treatment and prevention strategies, most individuals can return to their normal activities without long-term issues.
Stroke Rehabilitation: Conditions and SymptomsOrthopedic rehabilitation is a specialized branch of physiotherapy aimed at restoring function, strength, and mobility after musculoskeletal injuries, surgeries, or chronic orthopedic conditions. It plays a crucial role in helping patients recover from bone, joint, ligament, and muscle-related issues, ensuring improved quality of life and independence.
Common Conditions Treated:
- Post-fracture rehabilitation
- Post joint replacement surgeries (knee, hip, shoulder)
- Ligament injuries (e.g., ACL, MCL tears)
- Sports injuries (strains, sprains, dislocations)
- Arthritis (osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis)
- Spine disorders (spondylosis, disc herniation)
- Tendonitis and bursitis
- Frozen shoulder
- Post-casting stiffness or weakness
Key Symptoms That Require Ortho Rehab:
Pain and Inflammation:
- Persistent joint or muscle pain
- Swelling around affected areas
Mobility Issues:
- Limited range of motion
- Difficulty in walking, climbing stairs, or performing daily tasks
Muscle Weakness:
- Loss of strength in limbs or joints
- Fatigue with simple movements
Post-Surgical Symptoms:
- Stiffness or scar tissue formation
- Weakness after immobilization (like casting or bed rest)
Functional Limitations:
- Inability to return to sports or work
- Poor coordination and balance
Orthopedic rehabilitation is essential for individuals recovering from injuries, surgeries, or chronic conditions affecting bones and joints. Whether it’s regaining mobility after a knee replacement or building strength following a fracture, orthopedic physiotherapy helps reduce pain, restore function, and prevent long-term disability. Symptoms such as joint stiffness, muscle weakness, limited mobility, and chronic pain indicate the need for professional rehab. A personalized treatment plan—including exercises, manual therapy, pain relief techniques, and functional training—is key to a successful recovery and a return to active life.
Neurological rehabilitation (Neuro Rehab) is a comprehensive physiotherapy program designed to help individuals recover and regain function after damage to the nervous system. It plays a vital role in improving mobility, strength, coordination, and independence in patients affected by neurological conditions such as stroke, spinal cord injuries, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and cerebral palsy.
Common Neurological Conditions Treated:
- Stroke (Ischemic or Hemorrhagic)
- Spinal Cord Injuries
- Parkinson’s Disease
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Cerebral Palsy
- Traumatic Brain Injuries (TBI)
- Peripheral Neuropathy
- Bell’s Palsy
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome
- Motor Neuron Disease
Key Symptoms Requiring Neuro Rehabilitation:
Motor Deficits:
- Weakness or paralysis of limbs
- Inability to walk or maintain balance
- Loss of coordination and fine motor skills
Sensory Disturbances:
- Numbness or tingling in arms or legs
- Hypersensitivity to touch or temperature
Cognitive & Speech Issues:
- Memory loss or confusion
- Difficulty in speaking or understanding language (aphasia)
Spasticity & Muscle Stiffness:
- Increased muscle tone
- Difficulty in performing smooth movements
Postural & Gait Abnormalities:
- Stooped posture
- Shuffling walk or foot drop
Neuro rehabilitation focuses on helping individuals recover after damage to the brain, spinal cord, or peripheral nerves. It aims to restore movement, strength, balance, and coordination that may be affected due to neurological disorders. Patients often experience muscle weakness, loss of mobility, speech difficulties, or coordination issues. A structured rehab plan includes physiotherapy, balance training, strength exercises, neuromuscular re-education, and functional task training. With regular sessions and professional guidance, patients can regain independence, improve their daily functioning, and enhance their overall quality of life. Early intervention is key to maximizing recovery in neuro rehab.
Cardiac (or cardio) rehabilitation is a medically supervised program aimed at improving cardiovascular health after a heart-related event or diagnosis. It combines exercise training, lifestyle education, and emotional support to help individuals recover and reduce the risk of future heart problems.
Common Conditions Requiring Cardiac Rehabilitation:
- Heart attack (Myocardial Infarction)
- Coronary artery disease (CAD)
- Angina (chest pain)
- Heart failure
- Post-coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery
- Post-angioplasty or stent placement
- Cardiomyopathy
- Heart valve surgery
- Heart transplant recovery
Symptoms That Indicate Need for Cardiac Rehab:
Physical Symptoms:
- Shortness of breath with minimal exertion
- Chest pain or tightness (angina)
- Fatigue and low energy levels
- Swelling in legs and ankles (edema)
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat (palpitations)
- Dizziness or fainting spells
Exercise Intolerance:
- Inability to walk moderate distances
- Low stamina or endurance
- Breathlessness during daily activities
Psychological Symptoms:
- Anxiety or fear of another heart event
- Depression or mood swings
- Low confidence in physical abilities
Cardiac rehabilitation is essential for patients recovering from heart attacks, surgeries, or chronic heart diseases. It focuses on improving cardiovascular strength, reducing symptoms like fatigue, chest discomfort, and breathlessness, and preventing future cardiac events. Common signs that indicate the need for rehab include shortness of breath during mild activity, swelling in the legs, chest pain, and low energy. The program involves tailored physical activity, heart-healthy education, and stress management strategies. It empowers patients to safely regain strength, boost endurance, and adopt lifelong habits for heart health. With timely rehab and expert supervision, patients enjoy better recovery and reduced risk of complications.
Pulmonary rehabilitation is a structured program designed to help individuals with chronic lung diseases improve their quality of life and physical functioning. It addresses both the physical and psychological challenges of respiratory conditions, providing patients with the tools to manage their symptoms effectively.
Conditions Treated with Pulmonary Rehabilitation:
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- Emphysema
- Chronic Bronchitis
- Pulmonary Fibrosis
- Asthma (severe cases)
- Cystic Fibrosis
- Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
- Pulmonary Hypertension
- Sleep Apnea (associated with daytime fatigue)
- Post-surgical recovery (lung transplant, thoracic surgery)
- Lung Cancer (post-treatment rehabilitation)
- Sarcoidosis
- Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome (OHS)
- Bronchiectasis
Symptoms Addressed by Pulmonary Rehabilitation:
- Shortness of Breath (Dyspnea) – Difficulty breathing, especially during physical exertion.
- Chronic Cough – Persistent coughing, often productive of mucus.
- Fatigue – Overwhelming tiredness and lack of energy.
- Wheezing – High-pitched sound while breathing due to narrowed airways.
- Chest Tightness – A feeling of pressure or constriction in the chest.
- Cyanosis – Bluish discoloration of the lips or extremities due to low oxygen levels.
- Increased Mucus Production – Excessive sputum, leading to blocked airways.
- Recurrent Respiratory Infections – Increased frequency of pneumonia, bronchitis, or colds.
- Limited Physical Endurance – Reduced stamina and difficulty performing physical activities.
- Difficulty Sleeping – Sleep disturbances due to breathing difficulties or discomfort.
- Anxiety – Feelings of stress or fear associated with breathing difficulties.
- Depression – Emotional challenges from chronic illness and limited physical activity.
- Loss of Appetite – Reduced desire to eat due to breathlessness and fatigue.
- Swelling in the Legs – Due to fluid retention from pulmonary or heart problems.
- Memory and Concentration Issues – Cognitive difficulties related to chronic low oxygen levels.
Pulmonary rehabilitation plays a vital role in improving the symptoms of these conditions by combining physical exercises, breathing techniques, education, and emotional support. This approach helps patients gain better control over their illness and enhances their overall health.
Stroke rehabilitation is a crucial part of the recovery process for individuals who have experienced a stroke. It focuses on helping patients regain lost abilities and develop new strategies for managing daily activities. Stroke rehabilitation addresses both the physical and cognitive aspects of recovery, aiming to improve the quality of life and enhance independence.
Conditions Treated in Stroke Rehabilitation:
- Ischemic Stroke – Caused by a blockage in a blood vessel supplying the brain.
- Hemorrhagic Stroke – Results from a ruptured blood vessel in the brain.
- Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) – A temporary blockage in the brain’s blood supply, often referred to as a mini-stroke.
- Cerebral Venous Thrombosis (CVT) – A rare condition caused by a blood clot in the veins of the brain.
- Brainstem Stroke – A stroke occurring in the brainstem, affecting vital functions such as breathing and heart rate.
- Post-Stroke Spasticity – Muscle tightness or stiffness following a stroke, often impacting movement.
- Post-Stroke Aphasia – Difficulty in speaking, understanding, reading, or writing due to damage in the language-processing areas of the brain.
- Ataxia – Loss of muscle coordination, often affecting balance and movement.
- Hemianopia – Loss of vision in half of the visual field, often resulting from a stroke.
- Post-Stroke Depression – Emotional challenges such as sadness, anxiety, and a feeling of hopelessness that can occur after a stroke.
Symptoms Addressed by Stroke Rehabilitation:
Paralysis or Weakness – Loss of strength or movement, typically on one side of the body (hemiplegia).
Difficulty Walking – Impaired mobility or trouble maintaining balance.
Speech Impairment (Aphasia) – Difficulty in forming or understanding speech.
Memory Loss – Trouble recalling information or performing tasks that require cognitive recall.
Fatigue – Extreme tiredness that interferes with daily activities.
Pain or Discomfort – Chronic pain in limbs or muscles affected by the stroke.
Loss of Coordination – Difficulty with fine motor skills or performing precise movements.
Vision Problems – Blurred vision or loss of part of the visual field (hemianopia).
Emotional Instability – Mood swings, anxiety, or depression due to the impact of stroke.
Difficulty Swallowing (Dysphagia) – Trouble swallowing food or liquids, increasing the risk of choking or aspiration.
Stroke rehabilitation combines physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and psychological support to address these conditions and symptoms. The goal is to maximize recovery, promote independence, and improve the patient’s overall well-being.
Special Education refers to tailored instructional programs designed to meet the unique learning needs of children with developmental, intellectual, physical, emotional, or behavioral challenges. It provides structured learning with appropriate resources, accommodations, and therapeutic support to help every child reach their full academic and social potential.
Conditions Commonly Supported in Special Education:
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- Down Syndrome
- Learning Disabilities (Dyslexia, Dyscalculia, Dysgraphia)
- Cerebral Palsy
- Intellectual Disabilities
- Hearing Impairment
- Visual Impairment
- Emotional and Behavioral Disorders
- Speech and Language Disorders
Symptoms That Indicate the Need for Special Education:
- Delayed Speech or Communication Skills
- Difficulty in Reading, Writing, or Math
- Short Attention Span or Inattentiveness
- Poor Memory or Retention Skills
- Difficulty Following Instructions
- Frequent Tantrums or Behavioral Outbursts
- Challenges in Social Interaction or Peer Play
- Unusual Repetitive Behaviors or Movements
- Difficulty with Fine or Gross Motor Skills
- Lack of Progress in Regular Classroom Settings
Special education programs are crafted through Individualized Education Plans (IEPs), created by a team of educators, therapists, and parents. These plans include specialized teaching strategies, assistive technology, and therapies such as occupational, speech, or behavioral interventions. The goal is to empower children with challenges to achieve academic success and build confidence in a supportive, inclusive environment tailored to their specific learning styles and needs.
Speech Therapy is a specialized intervention designed to diagnose and treat communication disorders, speech impediments, and oral motor difficulties. It helps individuals of all ages improve their speech clarity, language comprehension, voice modulation, and swallowing functions.
Conditions Treated by Speech Therapy:
- Speech Delay
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- Stuttering (Fluency Disorder)
- Cerebral Palsy
- Aphasia (Post-Stroke Language Loss)
- Down Syndrome
- Apraxia of Speech
- Hearing Impairment
- Cleft Lip and Palate
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
Symptoms Indicating the Need for Speech Therapy:
- Delayed Speech Development
- Difficulty Pronouncing Words Clearly
- Limited Vocabulary for Age
- Struggles to Form Sentences
- Stammering or Stuttering
- Inability to Follow Verbal Instructions
- Slurred or Unclear Speech
- Hoarse or Raspy Voice
- Difficulty Swallowing (Dysphagia)
- Poor Social Communication Skills
Speech therapy typically begins with a detailed assessment to identify the individual’s communication challenges. Based on the diagnosis, a personalized therapy plan is created. Sessions may involve exercises to strengthen the muscles used in speech, activities to improve language comprehension, or the use of assistive devices. For children, therapy often includes play-based techniques, while adults may focus on regaining speech post-injury or illness. The ultimate goal is to enhance communication, boost confidence, and support better integration in academic, social, and professional settings.
Occupational Therapy (OT) is a holistic approach that helps individuals of all ages participate in meaningful daily activities (occupations) despite physical, cognitive, or emotional challenges. The aim is to promote independence, improve functional skills, and enhance quality of life.
Conditions Treated by Occupational Therapy:
- Cerebral Palsy
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- Stroke Recovery
- Arthritis
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
- Sensory Processing Disorder
- Parkinson’s Disease
- Down Syndrome
- Developmental Delays
- Spinal Cord Injury
Symptoms Indicating the Need for Occupational Therapy:
- Difficulty with Fine Motor Skills (e.g., writing, buttoning clothes)
- Challenges in Daily Self-Care Tasks (e.g., dressing, grooming)
- Poor Hand-Eye Coordination
- Delayed Motor Milestones in Children
- Difficulty Managing Emotions or Behaviors
- Problems with Sensory Integration (over- or under-reactivity)
- Poor Balance and Coordination
- Limited Social Interaction Skills
- Fatigue During Routine Activities
- Reduced Independence After Injury or Surgery
Occupational therapists assess a person’s physical, emotional, and environmental challenges to develop personalized intervention plans. These may include exercises to improve motor control, adaptive techniques for daily living, assistive devices, and strategies for better sensory regulation or cognitive functioning. OT empowers individuals to lead more independent and fulfilling lives by addressing the functional barriers that affect their ability to work, learn, play, or care for themselves and others.
Manual Therapy is a hands-on physiotherapy technique involving the manipulation and mobilization of muscles, joints, and soft tissues. It is primarily used to reduce pain, restore mobility, improve circulation, and aid recovery from injuries.
Conditions Treated by Manual Therapy:
- Back Pain (including lower back pain)
- Neck Pain
- Frozen Shoulder
- Tennis Elbow
- Sciatica
- Joint Stiffness
- Sports Injuries
- Post-surgical Joint Pain
- Arthritis
- Muscle Spasms or Tightness
Symptoms Indicating the Need for Manual Therapy:
- Chronic or Acute Muscular Pain
- Reduced Range of Motion
- Joint Stiffness or Locking
- Swelling or Inflammation Around Joints
- Numbness or Tingling Sensation
- Muscle Weakness
- Pain While Moving or Bending
- Muscle Imbalance or Postural Issues
- Difficulty in Daily Physical Activities
- Recurring Headaches Due to Muscle Tension
Manual therapy begins with a detailed assessment by a trained physiotherapist to identify the root cause of pain or dysfunction. Techniques like joint mobilization, soft tissue massage, myofascial release, and trigger point therapy are then applied to target the affected areas. This therapy enhances blood flow, reduces muscle tightness, and improves flexibility. Often used in conjunction with exercise and rehabilitation programs, manual therapy offers relief without medication or invasive procedures. It plays a crucial role in enhancing movement, restoring strength, and accelerating recovery in both acute and chronic musculoskeletal conditions.
Taping is a supportive technique used in physiotherapy and sports medicine to stabilize joints, support muscles, relieve pain, and prevent injury. It involves applying adhesive tape (rigid or elastic) to specific body parts to aid in movement, reduce strain, and facilitate healing.
Conditions Treated with Taping:
- Ankle Sprain
- Knee Ligament Injury (ACL/MCL sprain)
- Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis)
- Shoulder Impingement
- Shin Splints
- Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
- Achilles Tendinitis
- Lower Back Pain
- Plantar Fasciitis
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Symptoms Indicating the Use of Taping:
- Joint Instability
- Muscle Weakness
- Localized Swelling
- Sharp or Persistent Pain During Movement
- Recurrent Sports Injuries
- Poor Posture or Alignment
- Tingling or Numbness in Limbs
- Muscle Fatigue After Minimal Activity
- Restricted Range of Motion
- Feeling of Joint “Giving Way”
Taping techniques, such as Kinesio taping or rigid sports taping, provide structural support to injured or vulnerable areas while still allowing a degree of movement. Taping helps offload stress from tendons and ligaments, reduces inflammation, and improves proprioception (the sense of joint position). It is commonly used in athletes but is equally effective for non-athletic individuals dealing with musculoskeletal issues. A trained physiotherapist applies the tape with precision based on the injury’s nature, promoting faster recovery and safer movement.
Joint mobilization is a manual therapy technique used by physiotherapists to improve joint function, reduce pain, and increase the range of motion. It involves passive movements applied at various speeds and amplitudes to the joints, helping restore their normal movement patterns.
Conditions Treated with Joint Mobilization:
- Frozen Shoulder (Adhesive Capsulitis)
- Knee Osteoarthritis
- Cervical Spondylosis
- Lumbar Spondylosis
- Ankle Stiffness Post-Sprain
- Post-Fracture Joint Stiffness
- Hip Arthritis
- Wrist or Hand Stiffness
- Post-Operative Joint Immobilization
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (in remission phase)
Symptoms Indicating the Need for Joint Mobilization:
- Joint Stiffness
- Limited Range of Motion
- Pain During Joint Movement
- Clicking or Locking in the Joint
- Joint Swelling with Stiffness
- Muscle Tightness Around the Joint
- Impaired Daily Activities (e.g., walking, lifting)
- Poor Posture Due to Joint Dysfunction
- Weakness in the Affected Limb
- Feeling of Joint Being “Stuck” or “Blocked”
Joint mobilization is tailored to the individual’s condition and mobility level. It works by gently gliding or oscillating the joint surfaces to reduce stiffness, relieve pain, and enhance circulation in the joint capsule. This therapy is especially effective when combined with stretching and strengthening exercises. Patients recovering from surgery, injury, or chronic joint issues often benefit from this technique as it accelerates healing, promotes smoother movement, and reduces dependency on medications.
Exercise therapy is a fundamental component of physical rehabilitation aimed at improving strength, flexibility, endurance, coordination, and overall functional mobility. It is tailored to each patient’s condition and goals, whether for recovery, prevention, or general well-being.
Conditions Benefiting from Exercise:
- Osteoarthritis
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Hypertension
- Stroke Recovery
- Lower Back Pain
- Obesity
- Depression and Anxiety
- Post-Surgical Rehabilitation
- Cervical and Lumbar Spondylosis
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
Symptoms Indicating the Need for Exercise:
- Muscle Weakness
- Joint Stiffness
- Excess Fatigue
- Poor Balance or Coordination
- Restricted Mobility
- Shortness of Breath with Mild Activity
- Chronic Pain (Back, Neck, Joints)
- Low Energy Levels
- Postural Problems
- Reduced Ability to Perform Daily Tasks
Exercise plays a key role in managing and preventing a wide range of health conditions. Therapeutic exercises, whether aerobic, strength-based, flexibility-oriented, or balance-focused, are prescribed by physiotherapists or fitness professionals to match individual needs. In musculoskeletal conditions, exercises help restore joint mobility and muscle strength. For metabolic disorders like diabetes or obesity, regular activity improves insulin sensitivity and promotes weight control. In mental health conditions, exercise reduces stress and boosts mood. Whether recovering from surgery or managing a chronic illness, a structured exercise regimen enhances overall physical function, reduces symptoms, and improves quality of life significantly.
Electrotherapy involves the use of electrical energy for medical purposes, particularly in physiotherapy, to relieve pain, improve circulation, stimulate muscles, and promote healing. It includes modalities like TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation), IFT (Interferential Therapy), EMS (Electrical Muscle Stimulation), and ultrasound therapy.
Conditions Treated with Electrotherapy:
- Sciatica
- Frozen Shoulder
- Arthritis (Osteoarthritis & Rheumatoid Arthritis)
- Lumbar and Cervical Spondylosis
- Tennis Elbow
- Post-Surgical Pain and Swelling
- Muscle Atrophy
- Ligament Injuries
- Sports Injuries
- Chronic Back or Neck Pain
Symptoms Electrotherapy Can Help Relieve:
- Sharp or Radiating Pain
- Muscle Weakness
- Joint Stiffness
- Swelling and Inflammation
- Tingling or Numbness
- Limited Range of Motion
- Muscle Spasms
- Post-Trauma Discomfort
- Poor Circulation
- Delayed Healing of Soft Tissue
Electrotherapy is a non-invasive, drug-free approach that accelerates recovery. It works by sending mild electrical impulses to the affected area, which either blocks pain signals to the brain (as in TENS) or contracts the muscle to prevent wasting (as in EMS). It is highly effective in both acute and chronic musculoskeletal issues and often complements manual therapy and exercise for better outcomes. By reducing pain and inflammation, it helps patients move more comfortably and resume daily activities faster.
Magnetic therapy is a form of alternative treatment that uses static magnetic fields to improve blood flow, relieve pain, and enhance healing. It involves the application of magnets to the body, typically in the form of bracelets, pads, or therapeutic devices. While scientific evidence is still emerging, many individuals report symptom relief from regular magnetic therapy use.
Conditions That May Benefit from Magnetic Therapy:
- Arthritis (Osteoarthritis & Rheumatoid Arthritis)
- Chronic Back Pain
- Fibromyalgia
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Migraines and Tension Headaches
- Sports Injuries
- Tendonitis
- Neck and Shoulder Pain
- Plantar Fasciitis
- Insomnia and Fatigue
Symptoms Magnetic Therapy May Help Relieve:
- Persistent Joint Pain
- Inflammation and Swelling
- Stiffness in Muscles and Joints
- Chronic Fatigue
- Muscle Cramps
- Localized Numbness or Tingling
- Frequent Headaches
- Disturbed Sleep
- Poor Circulation
- Delayed Healing in Soft Tissue Injuries
Magnetic therapy is thought to work by affecting the body’s electromagnetic field, potentially improving cellular function and circulation. By increasing blood flow, it may help reduce inflammation, ease pain, and promote natural healing. It is commonly used as a complementary therapy alongside physiotherapy, acupuncture, and lifestyle modifications. Though not a replacement for medical treatment, it offers a non-invasive, gentle option for symptom management, especially in chronic conditions where long-term relief is sought.
Dry Needling and Acupuncture are minimally invasive therapies that use fine needles to stimulate specific points in the body. While acupuncture is rooted in traditional Chinese medicine, focusing on energy flow (Qi), dry needling is a modern technique targeting muscle trigger points to relieve pain and dysfunction.
Conditions Treated with Dry Needling & Acupuncture:
- Chronic Neck and Back P
- Shoulder Impingement or Frozen Shoulder
- Tennis Elbow / Golfer’s Elbow
- Knee Osteoarthritis
- Migraine and Tension Headaches
- Sciatica and Nerve Compression
- Fibromyalgia
- Plantar Fasciitis
- Myofascial Pain Syndrome
- TMJ Disorders (Jaw Pain)
Symptoms These Therapies Help Relieve:
- Sharp or Radiating Musculoskeletal Pain
- Stiffness in Joints and Muscles
- Muscle Spasms or Cramps
- Tingling or Numbness
- Reduced Range of Motion
- Fatigue and Low Energy
- Headaches and Facial Pain
- Chronic Inflammation
- Stress and Anxiety
- Sleep Disturbances
Dry needling works by targeting taut bands or “trigger points” in muscles, causing them to release and relax, improving movement and reducing pain. Acupuncture, on the other hand, balances energy pathways and promotes holistic healing. Both treatments can increase circulation, reduce inflammation, and stimulate the body’s natural painkillers. When combined with physiotherapy and lifestyle changes, they can accelerate recovery in various acute and chronic conditions, enhancing physical and emotional well-being.
Physiotherapy for rheumatoid arthritis focuses on reducing joint pain, controlling inflammation, improving flexibility, and maintaining independence. It helps prevent deformities, strengthens muscles around joints, and supports overall function and mobility.
Common Conditions Treated:
- Chronic joint inflammation
- Muscle stiffness and fatigue
- Deformities in fingers, wrists, knees
- Reduced joint range of motion
- Muscle weakness and atrophy
- Postural imbalance
- Joint contractures
Symptoms Managed:
- Persistent joint pain
- Morning stiffness (lasting more than 30 minutes)
- Swollen, warm, or tender joints
- Reduced strength and grip
- Fatigue and general weakness
- Difficulty performing daily tasks
- Joint deformities (e.g., ulnar drift)
- Limited flexibility and movement
A brain stroke, or cerebrovascular accident (CVA), occurs when there is a sudden disruption in the blood supply to the brain, leading to brain cell damage. The stroke may be ischemic (caused by a blockage) or hemorrhagic (caused by bleeding). Stroke survivors often experience various physical and cognitive impairments, making rehabilitation essential for recovery. Physiotherapy plays a pivotal role in helping individuals regain motor function, improve balance, and enhance quality of life. The severity and outcomes of a stroke depend on the type, location, and size of the brain injury. Early intervention with physiotherapy can significantly enhance recovery.
Common Conditions Treated through Physiotherapy Post-Stroke:
- Hemiplegia (paralysis on one side of the body)
- Hemiparesis (weakness on one side of the body)
- Muscle spasticity or rigidity
- Balance and coordination issues
- Gait abnormalities and walking difficulties
- Loss of fine motor skills (difficulty using hands)
- Cognitive impairments (memory loss, difficulty concentrating)
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Speech and language impairments (aphasia)
- Joint contractures due to immobility
Symptoms of Stroke Managed by Physiotherapy:
- Sudden numbness or weakness, especially on one side of the body
- Slurred speech or difficulty speaking
- Loss of coordination and balance
- Difficulty walking or standing
- Facial drooping or uneven smile
- Impaired vision or blindness in one or both eyes
- Severe headache, often with no known cause
- Sudden confusion or trouble understanding speech
- Memory problems or difficulty performing daily tasks
Lumbar spondylosis, often referred to as degenerative disc disease or osteoarthritis of the spine, is a condition that affects the lower back (lumbar spine). It involves the wear and tear of the intervertebral discs, joints, and bones, leading to pain, stiffness, and limited movement. The condition primarily affects individuals as they age, with the natural degeneration of spinal structures over time. Early detection and appropriate management, including physiotherapy, can help alleviate symptoms and improve the quality of life.
Conditions Associated with Lumbar Spondylosis:
- Degeneration of Intervertebral Discs: The discs between the vertebrae lose hydration and elasticity, leading to reduced shock absorption and pain.
- Bone Spurs (Osteophytes): Over time, the spine may develop bone spurs or growths, which can press on nerves, causing pain.
- Facet Joint Osteoarthritis: The small joints at the back of the spine may wear down, leading to inflammation and stiffness.
- Spinal Stenosis: Narrowing of the spinal canal due to disc degeneration or bone spurs can compress the spinal cord or nerves, leading to neurological symptoms.
- Herniated Disc: A disc may bulge or rupture, pressing on surrounding nerves, causing pain or numbness in the legs.
Symptoms of Lumbar Spondylosis:
- Lower Back Pain: A constant dull ache or sharp pain in the lower back, often worsened by activity or prolonged sitting.
- Stiffness: Difficulty bending, twisting, or performing routine activities due to stiffness in the lower back.
- Sciatica: Pain radiating down one or both legs due to compression of the sciatic nerve.
- Numbness or Tingling: Sensory changes in the legs or feet caused by nerve compression.
- Weakness: Reduced strength in the legs, making it difficult to walk or stand for long periods.
- Reduced Range of Motion: Difficulty in bending, stretching, or moving the lower back freely.
- Muscle Spasms: Sudden, painful contractions in the muscles surrounding the spine.
Lumbar spondylosis is a common condition that arises due to the natural aging process and wear and tear of the spine. Its symptoms can significantly affect mobility and quality of life. Early intervention through physiotherapy, lifestyle modifications, and, in some cases, surgical treatment can help manage the condition effectively, improving pain relief, flexibility, and overall function.
Orthopedic rehabilitation is a specialized branch of physiotherapy aimed at restoring function, strength, and mobility after musculoskeletal injuries, surgeries, or chronic orthopedic conditions. It plays a crucial role in helping patients recover from bone, joint, ligament, and muscle-related issues, ensuring improved quality of life and independence.
Common Conditions Treated:
- Post-fracture rehabilitation
- Post joint replacement surgeries (knee, hip, shoulder)
- Ligament injuries (e.g., ACL, MCL tears)
- Sports injuries (strains, sprains, dislocations)
- Arthritis (osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis)
- Spine disorders (spondylosis, disc herniation)
- Tendonitis and bursitis
- Frozen shoulder
- Post-casting stiffness or weakness
Key Symptoms That Require Ortho Rehab:
Pain and Inflammation:
- Persistent joint or muscle pain
- Swelling around affected areas
Mobility Issues:
- Limited range of motion
- Difficulty in walking, climbing stairs, or performing daily tasks
Muscle Weakness:
- Loss of strength in limbs or joints
- Fatigue with simple movements
Post-Surgical Symptoms:
- Stiffness or scar tissue formation
- Weakness after immobilization (like casting or bed rest)
Functional Limitations:
- Inability to return to sports or work
- Poor coordination and balance
A spinal cord injury (SCI) is a serious condition that results from damage to the spinal cord, which can disrupt communication between the brain and the rest of the body. This type of injury can be traumatic (from accidents or falls) or non-traumatic (due to infections, tumors, or degenerative diseases). The severity and location of the injury determine the extent of impairment—ranging from temporary sensory issues to complete paralysis. Early intervention, rehabilitation, and physiotherapy are key in improving functional outcomes and quality of life.
Conditions Related to Spinal Cord Injury:
- Trauma from accidents, falls, or violence
- Tumors pressing on the spinal cord
- Infections like tuberculosis or meningitis
- Degenerative spinal disorders
- Autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis
Symptoms of Spinal Cord Injury:
- Paralysis: Partial or complete loss of movement in limbs (paraplegia or quadriplegia)
- Muscle Weakness or uncontrolled muscle spasms
- Loss of Fine Motor Skills in hands and fingers
- Decreased Reflexes or exaggerated reflex activity
Sensory Symptoms:
- Numbness or Tingling in the limbs
- Loss of Sensation below the site of injury
- Pain or burning sensations
Autonomic Symptoms:
- Bladder and Bowel
- Breathing Difficulties (in high cervical injuries)
- Blood Pressure Instability
- Sexual Dysfunction Dysfunction
Spinal cord injury (SCI) rehabilitation focuses on helping individuals recover as much function as possible and adapt to changes caused by the injury. It includes therapies aimed at improving mobility, self-care, and quality of life for those affected by spinal cord damage.
Conditions Treated in Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation:
- Complete Spinal Cord Injury – Total loss of sensation and movement below the level of injury.
- Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury – Partial loss of sensation or movement.
- Paraplegia – Paralysis of the lower limbs, often caused by thoracic, lumbar, or sacral injuries.
- Tetraplegia (Quadriplegia) – Paralysis of both the upper and lower limbs, usually due to cervical injuries.
- Spinal Shock – Temporary loss of reflexes and muscle function immediately after the injury.
- Autonomic Dysreflexia – A potentially life-threatening condition involving high blood pressure and other symptoms triggered by stimuli below the injury.
- Pressure Ulcers (Bedsores) – Skin damage caused by prolonged pressure, often a concern in SCI patients with reduced mobility.
- Spasticity – Muscle stiffness or involuntary muscle spasms.
- Neurogenic Bladder/Bowel – Loss of bladder and bowel control due to nerve damage.
- Chronic Pain – Neuropathic pain, often due to nerve damage at or below the level of injury.
Symptoms Addressed by Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation:
- Paralysis – Loss of voluntary muscle movement below the injury site.
- Sensory Loss – Reduced or complete loss of sensation below the injury.
- Loss of Coordination – Difficulty controlling body movements.
- Difficulty Breathing – Respiratory issues due to chest or cervical spinal injuries.
- Spasms – Involuntary muscle contractions.
- Difficulty performing daily tasks
- Spasms – Involuntary muscle contractions.
- Pain – Acute or chronic pain at or below the injury level.
- Bladder/Bowel Dysfunction – Inability to control urination or defecation.
- Pressure Sores – Ulcers from prolonged sitting or lying down.
- Fatigue – Persistent tiredness and weakness, common after SCI.
- Depression – Emotional distress from the physical and psychological impact of SCI.
Rehabilitation aims to restore as much function as possible and help individuals adjust to daily life, focusing on mobility, independence, and well-being.
Pre and post-surgery care is essential for ensuring the success of surgical procedures and promoting effective recovery. Managing conditions before and after surgery helps reduce complications and supports the healing process.
Conditions Addressed Pre and Post Surgery:
- Infection Risk – Increased likelihood of infection before or after surgery.
- Blood Clotting Disorders – Conditions like deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or clotting issues that may affect recovery.
- Heart Disease – Pre-existing heart conditions requiring careful monitoring during and after surgery.
- Diabetes – Blood sugar levels need to be controlled to prevent complications.
- Obesity – Excess weight that can affect anesthesia and wound healing.
- Chronic Respiratory Conditions – Conditions like COPD that may impact breathing during and after surgery.
- High Blood Pressure – Hypertension that needs to be controlled to avoid complications.
- Kidney Disease – Kidney function needs monitoring, especially with anesthesia.
- Previous Surgeries or Scarring – Past surgical scars or complications that could affect recovery.
- Medication Interactions – Ensuring medications do not interfere with anesthesia or post-op care.
Symptoms Addressed Pre and Post Surgery:
- Pain – Discomfort before and after surgery, requiring pain management.
- Swelling – Common after surgery, especially in the affected area.
- Fever – Possible sign of infection before or after surgery.
- Nausea and Vomiting – Common after anesthesia or pain medication.
- Fatigue – Feeling of extreme tiredness, often present before and after surgery.
- Shortness of Breath – Breathing issues can occur due to anesthesia or complications.
- Bleeding – Excessive bleeding during or after surgery.
- Dizziness – Often caused by anesthesia or blood pressure changes.
- Loss of Appetite – Common before and after surgery, often due to stress or medication.
- Difficulty Sleeping – Both pre and post-surgery anxiety or discomfort can disrupt sleep.
Effective pre and post-surgery care involves addressing these conditions and symptoms to improve recovery outcomes and ensure patient safety.
Dated physiotherapy refers to the rehabilitation or treatment approach that has been used over time to address various musculoskeletal and neurological conditions. While modern techniques have advanced, many traditional physiotherapy methods are still relevant and effective in managing a range of conditions. These include both acute injuries and chronic diseases that affect mobility, function, and quality of life.
Conditions Treated with Dated Physiotherapy:
- Osteoarthritis – Degenerative joint disease causing pain and stiffness, commonly in the knees, hips, and hands.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis – An autoimmune disorder causing inflammation and pain in joints.
- Back Pain – Chronic or acute discomfort in the lower or upper back.
- Neck Pain – Stiffness and discomfort in the cervical spine region.
- Muscle Strains – Injuries to muscle fibers from overuse or sudden movements.
- Sprains – Ligament injuries, often caused by twisting or overextension of joints.
- Sciatica – Pain radiating along the sciatic nerve, often due to disc herniation.
- Post-Surgical Rehabilitation – Recovery after surgeries such as joint replacements or spinal procedures.
- Post-Stroke Rehabilitation – Therapy for regaining mobility and function after a stroke.
- Tendinitis – Inflammation of tendons, typically in the shoulder, elbow, or knee.
Symptoms Addressed by Dated Physiotherapy:
- Pain – Acute or chronic discomfort in muscles, joints, or bones.
- Stiffness – Limited joint or muscle movement, often due to inflammation or injury.
- Swelling – Inflammation or fluid retention in joints or tissues.
- Weakness – Reduced strength or muscle function, commonly after injury or surgery.
- Reduced Range of Motion – Inability to fully extend or flex a joint or muscle.
- Impaired Balance – Difficulty maintaining stable posture, especially after injury or stroke.
- Fatigue – Tiredness or lack of energy, often due to prolonged pain or healing.
- Numbness or Tingling – Abnormal sensations caused by nerve compression or damage.
- Decreased Mobility – Difficulty moving or walking due to pain, injury, or weakness.
- Spasms – Involuntary muscle contractions or cramps, often following injury.
Dated physiotherapy techniques, including manual therapy, heat/cold applications, and exercises, continue to be effective in treating these conditions and symptoms, facilitating recovery, improving mobility, and managing chronic pain.
Post-surgery rehabilitation plays a crucial role in helping individuals recover from various surgeries by restoring function, reducing pain, and improving mobility. The rehabilitation process is essential for ensuring a smooth recovery and preventing complications after surgery.
Conditions Addressed by Post-Surgery Rehabilitation:
- Joint Replacement (Hip/Knee) – Post-surgical recovery after joint replacement to restore mobility and reduce pain.
- Spinal Surgery – Rehabilitation following procedures like spinal fusion or disc replacement to improve flexibility and strength.
- Fractures (Bone Surgery) – Rehabilitation after bone fractures to restore full function and strength.
- Cardiac Surgery (e.g., Bypass, Valve Replacement) – Recovery after heart surgeries to improve circulation, strength, and endurance.
- Abdominal Surgery – Post-surgical recovery from abdominal procedures, such as appendectomy or hernia repair.
- Breast Cancer Surgery (Mastectomy) – Rehabilitation for strength, mobility, and psychological support after breast cancer surgery.
- Arthroscopic Surgery – Recovery after minimally invasive joint surgeries to regain full function and reduce swelling.
- Cataract Surgery – Post-operative rehabilitation to restore vision and reduce discomfort.
- Bariatric Surgery – Rehabilitation to address dietary changes, physical activity, and psychological adjustments after weight-loss surgery.
- Plastic or Reconstructive Surgery – Recovery after surgeries like face-lifts or skin grafts, aimed at restoring physical appearance and function.
Symptoms Addressed by Post-Surgery Rehabilitation:
- Pain – Persistent discomfort that can arise during the recovery period.
- Swelling – Inflammation around the surgical area that can affect healing.
- Stiffness – Reduced movement or flexibility in joints or muscles post-surgery.
- Weakness – Muscle strength loss due to inactivity or surgery.
- Fatigue – Feeling of extreme tiredness during recovery.
- Nausea – Common after surgeries involving anesthesia.
- Reduced Mobility – Limited movement or difficulty walking after surgery.
- Scarring – Formation of visible scars that may affect range of motion or appearance.
- Breathing Difficulties – Especially after chest or abdominal surgeries.
- Emotional Stress – Anxiety, depression, or frustration due to changes in physical appearance or lifestyle.
Post-surgery rehabilitation involves physical therapy, psychological support, and sometimes lifestyle changes, all aimed at promoting faster recovery, enhancing functional capacity, and improving overall well-being.
Sensory Symptoms:
- Numbness or Tingling in the limbs
- Loss of Sensation below the site of injury
- Pain or burning sensations
Autonomic Symptoms:
- Bladder and Bowel
- Breathing Difficulties (in high cervical injuries)
- Blood Pressure Instability
- Sexual Dysfunction Dysfunction
Neck pain is a common issue that can range from mild discomfort to severe pain, often affecting daily activities. It can be caused by various underlying conditions and manifests in different symptoms. Understanding these conditions and symptoms helps in effective diagnosis and treatment.
Conditions Causing Neck Pain:
- Cervical Spondylosis – Age-related degeneration of the cervical spine, leading to pain and stiffness.
- Herniated Disc – Displacement of the disc between cervical vertebrae, causing nerve compression.
- Whiplash – Injury to the neck muscles and ligaments, often due to car accidents or sudden jerks.
- Cervical Stenosis – Narrowing of the spinal canal in the neck, putting pressure on the spinal cord.
- Muscle Strain – Overuse or injury of neck muscles due to poor posture, lifting, or sudden movements.
- Pinched Nerve – Compression of a nerve in the cervical spine, leading to pain and numbness.
- Osteoarthritis – Degeneration of cartilage in the neck joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
- Tension Headaches – Headaches caused by muscle tension in the neck and shoulders.
- Fibromyalgia – A chronic condition causing widespread musculoskeletal pain, including neck pain.
- Infection or Abscess – Bacterial infections or abscesses in the neck can lead to swelling and pain.
Symptoms of Neck Pain:
- Stiffness – Reduced range of motion or difficulty moving the neck.
- Muscle Spasms – Involuntary muscle contractions leading to pain and tightness.
- Radiating Pain – Pain that spreads to the shoulders, arms, or upper back.
- Numbness or Tingling – Sensations of numbness or tingling in the arms or hands, often caused by nerve compression.
- Headaches – Pain that starts in the neck and radiates to the head.
- Pain with Movement – Increased pain when turning or tilting the neck.
- Weakness – Weakness in the arms or hands, often due to nerve involvement.
- Limited Mobility – Difficulty performing everyday tasks due to restricted neck movement.
- Swelling or Tenderness – Visible swelling or tenderness around the neck area.
- Burning Sensation – A burning feeling along the neck, shoulders, or arms, often due to nerve irritation.
Neck pain can result from various causes, and treatment typically includes physical therapy, medications, and lifestyle adjustments to alleviate pain and improve mobility.
Hydrotherapy, also known as water therapy, utilizes the physical properties of water (buoyancy, resistance, temperature) to treat a variety of health conditions. It involves exercises and treatments performed in warm water and is used to improve circulation, alleviate pain, and promote rehabilitation.
Conditions Treated with Hydrotherapy:
- Arthritis (Osteoarthritis & Rheumatoid Arthritis)
- Chronic Back Pain
- Fibromyalgia
- Sports Injuries (Sprains, Strains)
- Post-Surgical Rehabilitation
- Muscle and Joint Stiffness
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Cerebral Palsy
- Stroke Recovery
- Stress and Anxiety
Symptoms Hydrotherapy Helps Relieve:
- Muscle Weakness
- Joint Pain and Swelling
- Limited Range of Motion
- Chronic Inflammation
- Stiffness in Limbs
- Tight or Sore Muscles
- Fatigue
- Balance Issues
- Post-Traumatic Pain
- Burning Sensation – A burning feeling along the neck, shoulders, or arms, often due to nerve irritation.
Neck pain can result from various causes, and treatment typically includes physical therapy, medications, and lifestyle adjustments to alleviate pain and improve mobility.
Strengthening programs focus on building muscle strength and improving functional movement to enhance overall health. These programs typically include exercises targeting specific muscle groups to improve muscle mass, endurance, and stability. They are used to treat a variety of conditions and symptoms related to muscle weakness, injury, and chronic pain.
Conditions Treated with Strengthening Programs:
- Osteoarthritis
- Muscle Weakness (General or Post-Injury)
- Chronic Back Pain
- Post-Surgical Rehabilitation (e.g., joint replacement)
- Fibromyalgia
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Sports Injuries
- Cerebral Palsy
- Stroke Recovery
- Postural Imbalances
Symptoms Strengthening Programs Help Relieve:
- Weakness in Muscles and Joints
- Chronic Pain (Back, Neck, etc.)
- Stiffness and Limited Range of Motion
- Muscle Atrophy
- Fatigue
- Difficulty with Mobility or Walking
- Impaired Balance and Coordination
- Post-Surgical Discomfort
- Numbness and Tingling in Extremities
- Difficulty Performing Daily Activities
Strengthening programs are designed to rebuild muscle strength, improve posture, and increase functional movement. By targeting weakened or underused muscle groups, they help alleviate pain, enhance mobility, and prevent further injury. These exercises also help increase flexibility and endurance, contributing to better overall health. Strengthening programs are commonly used in rehabilitation settings, especially after surgery or injury, and are crucial for individuals with chronic conditions like arthritis or neurological disorders. When performed under professional supervision, strengthening exercises can significantly improve a patient’s quality of life by restoring movement, reducing pain, and preventing future complications.
Pre and postnatal physiotherapy is specifically designed to help women navigate the physical challenges of pregnancy and recovery after childbirth. These therapies focus on improving posture, strengthening muscles, and promoting recovery by addressing musculoskeletal issues and preventing long-term complications.
Conditions Treated with Pre and Postnatal Physiotherapy:
- Pelvic Girdle Pain (PGP)
- Lower Back Pain
- Diastasis Recti (Abdominal Separation)
- Postpartum Incontinence
- Sciatica
- Round Ligament Pain
- Pubic Symphysis Dysfunction (PSD)
- Perineal Tears or Episiotomy Recovery
- Coccyx Pain (Tailbone Pain)
- Posture Problems (Due to Pregnancy Weight Shift)
Symptoms Relieved by Pre and Postnatal Physiotherapy:
- Lower Back and Pelvic Pain
- Abdominal Weakness or Tightness
- Difficulty with Walking or Standing for Long Periods
- Urinary Incontinence
- Reduced Flexibility and Range of Motion
- Pain or Discomfort in the Hips and Legs
- Muscle Fatigue and Weakness
- Difficulty Lifting or Carrying Objects
- Posture Deformities or Misalignment
- Swelling in the Legs and Feet
Pre and postnatal physiotherapy helps women cope with the physical strain pregnancy places on the body, especially as it affects the pelvis, lower back, and abdomen. In the prenatal phase, therapy aims to alleviate discomforts like back pain, sciatica, and PGP, while promoting strength and flexibility. After childbirth, physiotherapy focuses on rebuilding core strength, correcting postural issues, and managing conditions like incontinence or diastasis recti. These therapies also assist in recovery following a cesarean or vaginal delivery, speeding up the healing process and preventing long-term complications.
Respiratory rehabilitation is a comprehensive program designed to improve the quality of life for individuals with chronic respiratory conditions. It focuses on physical exercises, breathing techniques, education, and psychological support to help manage symptoms, increase lung function, and improve overall well-being.
Conditions Treated with Respiratory Rehabilitation:
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- Asthma
- Pulmonary Fibrosis
- Cystic Fibrosis
- Sleep Apnea
- Lung Cancer (post-surgery rehabilitation)
- Emphysema
- Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)
- Post-COVID-19 Lung Recovery
- Posture Problems (Due to Pregnancy Weight Shift)
- Post-COVID-19 Lung Recovery
Symptoms Improved with Respiratory Rehabilitation:
- Shortness of Breath (Dyspnea)
- Chronic Cough
- Fatigue
- Chest Tightness
- Wheezing
- Decreased Exercise Tolerance
- Inability to Perform Daily Activities (due to breathing issues)
- Poor Sleep Quality (due to breathing difficulties)
- Frequent Respiratory Infections
- Decreased Quality of Life
Respiratory rehabilitation is a crucial aspect of managing chronic lung conditions. It helps individuals cope with symptoms like shortness of breath, fatigue, and chronic coughing. Through tailored exercises, education, and respiratory techniques (e.g., pursed-lip breathing), patients improve their lung capacity and endurance. Rehabilitation also aids in reducing the frequency of respiratory infections, promoting better sleep, and improving overall daily function. For patients recovering from surgery or illness (like COVID-19), respiratory rehabilitation plays a vital role in restoring lung function and preventing long-term complications. Through consistent management and physical conditioning, respiratory rehabilitation enhances overall quality of life and helps patients live more independently.
COVID-19 is caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, and its effects can range from mild to severe, affecting various organs in the body. The virus primarily impacts the respiratory system but can also lead to complications involving the heart, kidneys, and more. Post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC), also known as “long COVID,” can persist even after the acute infection resolves.
Conditions Associated with COVID-19:
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
- Pneumonia
- Acute Kidney Injury
- Cardiac Arrhythmias
- Myocarditis
- Thromboembolism (Blood Clots)
- Cerebrovascular Events (e.g., Stroke)
- Liver Dysfunction
- Sepsis
- Long COVID (Post-COVID Syndrome)
Symptoms of COVID-19:
- Fever or Chills
- Cough
- Shortness of Breath or Difficulty Breathing
- Fatigue
- Loss of Taste or Smell
- Muscle or Body Aches
- Sore Throat
- Congestion or Runny Nose
- Headache
- Nausea or Vomiting
COVID-19 presents a wide range of symptoms, from mild to severe. The most common early signs include fever, cough, and fatigue. Respiratory issues such as shortness of breath or difficulty breathing are also common, particularly in more severe cases. As the disease progresses, complications such as pneumonia, ARDS, or even kidney and heart problems can develop. Long COVID refers to persistent symptoms like fatigue, brain fog, and respiratory issues that continue long after the acute infection has resolved. Even mild cases can lead to lingering effects, which is why post-COVID care, including rehabilitation and ongoing monitoring, is crucial for full recovery.
Physiotherapy is a vital treatment for a wide range of conditions, addressing musculoskeletal, neurological, and cardiovascular issues. It helps manage pain, improve movement, and promote overall health through physical exercises, manual therapy, and other rehabilitation techniques.
Conditions Treated with Physiotherapy:
- Osteoarthritis
- Chronic Back Pain
- Sprains and Strains
- Fractures
- Post-surgical Rehabilitation
- Sciatica
- Stroke Rehabilitation
- Cerebral Palsy
- Postural Dysfunction
- Sports Injuries
Symptoms Improved by Physiotherapy:
- Muscle Weakness
- Limited Range of Motion
- Chronic Pain
- Stiffness and Tightness in Joints
- Balance Issues
- Numbness or Tingling Sensation
- Difficulty Walking or Moving
- Swelling and Inflammation
- Fatigue
- Reduced Flexibility
Physiotherapy helps individuals recover from both acute and chronic conditions. For musculoskeletal problems like osteoarthritis, back pain, or post-surgical rehabilitation, physiotherapists use targeted exercises and manual therapy to restore mobility and alleviate pain. Neurological conditions, such as stroke or cerebral palsy, benefit from specialized programs aimed at improving coordination and strength. Symptoms like muscle weakness, stiffness, and balance issues are commonly addressed through tailored physiotherapy exercises. Regular sessions help increase strength, reduce pain, and enhance flexibility, ultimately improving the quality of life for those affected.
Alchemy Physiotherapy is dedicated to helping patients overcome a variety of musculoskeletal and neurological conditions. Patients often experience symptoms such as chronic pain, stiffness, and muscle weakness, which can significantly limit daily activities. Conditions like lower back pain, neck pain, and sports injuries are common reasons people seek physiotherapy treatment, while ailments such as osteoarthritis or frozen shoulder can lead to limited range of motion and difficulty performing simple tasks. Physiotherapists assess and treat symptoms such as numbness, tingling, swelling, and balance problems, offering tailored rehabilitation programs to reduce discomfort and restore normal function.
Common Conditions Treated by Alchemy Physiotherapy:
- Lower Back Pain
- Neck Pain
- Osteoarthritis
- Sciatica
- Sports Injuries
- Frozen Shoulder
- Post-Surgical Rehabilitation
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Tendonitis
- Postural Dysfunction
Common Symptoms Addressed:
- Chronic Pain
- Stiffness
- Weakness in Muscles
- Numbness and Tingling
- Swelling or Inflammation
- Limited Range of Motion
- Fatigue
- Balance Problems
- Shooting Pains
- Headaches and Migraines
For patients recovering from surgery, post-surgical rehabilitation is crucial to regain strength and mobility. Alchemy Physiotherapy also addresses tendonitis and carpal tunnel syndrome, focusing on reducing inflammation and improving joint function. The center emphasizes individualized care for both acute and chronic conditions, helping patients manage symptoms like headaches, shooting pains, and fatigue. Through hands-on techniques and therapeutic exercises, Alchemy Physiotherapy works toward alleviating symptoms, improving posture, and enhancing overall well-being.
Physiotherapy helps individuals recover from both acute and chronic conditions. For musculoskeletal problems like osteoarthritis, back pain, or post-surgical rehabilitation, physiotherapists use targeted exercises and manual therapy to restore mobility and alleviate pain. Neurological conditions, such as stroke or cerebral palsy, benefit from specialized programs aimed at improving coordination and strength. Symptoms like muscle weakness, stiffness, and balance issues are commonly addressed through tailored physiotherapy exercises. Regular sessions help increase strength, reduce pain, and enhance flexibility, ultimately improving the quality of life for those affected.
Apraxia of Speech is a motor speech disorder where a person has difficulty planning and coordinating the movements needed for speech. The condition affects the brain’s ability to send correct signals to the muscles responsible for speech, making it difficult for individuals to speak clearly, even though they may know what they want to say.
Conditions Associated with Apraxia of Speech:
- Stroke
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
- Dementia (e.g., Alzheimer’s)
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- Cerebral Palsy
- Neurodegenerative Disorders
- Pediatric Apraxia of Speech (Childhood Apraxia of Speech)
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Parkinson’s Disease
- Genetic Syndromes (e.g., Rett Syndrome)
Symptoms of Apraxia of Speech:
- Inconsistent Speech Errors
- Difficulty Pronouncing Words
- Groping Movements of the Mouth
- Slow or Halting Speech
- Difficulty with Proper Stress or Intonation
- Difficulty Coordinating Mouth and Lip Movements
- Substituting One Sound for Another
- Difficulty Saying Complex Words or Phrases
- Speech May be Unintelligible
- Normal Comprehension, but Difficulty Expressing Words
Apraxia of speech can be caused by damage to the areas of the brain responsible for motor speech control, including those affected by stroke, brain injury, or neurodegenerative conditions like Parkinson’s or multiple sclerosis. Individuals with this condition may exhibit difficulty with speech clarity, pronunciation, and coordination of mouth movements. Speech can be slow or halting, with sounds being substituted, omitted, or distorted. In some cases, the speech errors may be inconsistent, even for the same word. This can significantly impact an individual’s ability to communicate, although their comprehension and intelligence remain intact. Early speech therapy is essential in managing apraxia, focusing on techniques to improve articulation and speech fluency.
Physiotherapy helps individuals recover from both acute and chronic conditions. For musculoskeletal problems like osteoarthritis, back pain, or post-surgical rehabilitation, physiotherapists use targeted exercises and manual therapy to restore mobility and alleviate pain. Neurological conditions, such as stroke or cerebral palsy, benefit from specialized programs aimed at improving coordination and strength. Symptoms like muscle weakness, stiffness, and balance issues are commonly addressed through tailored physiotherapy exercises. Regular sessions help increase strength, reduce pain, and enhance flexibility, ultimately improving the quality of life for those affected.
Lab tests are diagnostic tools that involve the analysis of biological samples such as blood, urine, saliva, or tissue to help healthcare professionals assess an individual’s health status, diagnose conditions, monitor ongoing diseases, and evaluate the effectiveness of treatments. These tests provide valuable information about various bodily functions, enabling accurate diagnoses and better decision-making for patient care.
Common Types of Lab Tests:
Blood Tests:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): Measures red and white blood cell counts, hemoglobin, and platelets to assess overall health and detect disorders like anemia, infection, or leukemia.
- Lipid Profile: Measures cholesterol and triglyceride levels to assess the risk of heart disease.
- Blood Glucose Test: Monitors blood sugar levels to diagnose or manage diabetes.
Urine Tests:
- Urinalysis: Analyzes urine for signs of kidney disease, diabetes, or urinary tract infections (UTIs).
- Creatinine Clearance Test: Measures kidney function by evaluating how well creatinine is cleared from the blood.
Genetic Tests:
- DNA Testing: Identifies genetic predispositions to conditions such as cancer, heart disease, or inherited disorders.
Hormonal Tests:
- Thyroid Function Tests: Assesses thyroid health by measuring hormones like TSH, T3, and T4.
- Pregnancy Test: Measures levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) to confirm pregnancy.
Importance of Lab Tests:
Lab tests play a critical role in preventing, diagnosing, and treating diseases. They help identify risk factors early, guide treatment plans, and monitor disease progression. Regular lab tests can aid in early detection of conditions such as cancer, diabetes, or infections, ultimately improving health outcomes. Lab results should always be interpreted by a healthcare professional, as they consider the individual’s symptoms, medical history, and overall health when making a diagnosis.

About Dr. Preksha Singh – CEO & Expert Home Physiotherapist
Dr. Preksha Singh we bring expert physiotherapy to your doorstep, offering compassionate, personalized care right in the comfort of your home. Led by Dr. Preksha, one of the best female physiotherapists in Crossing Republik, Noida Extension, Noida, Vasundhara, and Vaishali (Ghaziabad),
Meet Our Doctors

Dr. kamran Chaudhary
B.P.T,M.P.T (Neuro)

Dr. kamran Chaudhary
B.P.T,M.P.T (Neuro)

Dr. Muin Akhlaq PT
Cupping Therapist

Dr. kirti Nagar
BPT,MPT (Ortho)

Dr. kirti Nagar
BPT,MPT (Ortho)

DR. ABHIMANYU
BPT, OMT(LONDON), COMT, CDNT, NSCA

DR. ABHIMANYU
BPT, OMT(LONDON), COMT, CDNT, NSCA

Dr. Madhukar
BPT and MPT (Neuro)

Dr. Madhukar
BPT and MPT (Neuro)

Dr. Nikcy Roy
B.P.T

Dr. DIVAS GUPTA
(STRENGTH AND CONDITIONING COACH)

Dr. DIVAS GUPTA
(STRENGTH AND CONDITIONING COACH)

Dr. Ankansha
B.P.T

Dr. Ankansha
B.P.T

Dr. kajal
Bachelor in occupational therapy Master in occupational therapy

Dr. kajal
Bachelor in occupational therapy Master in occupational therapy

Dr. Jaya
B.P.T,M.P.T (sports)

Dr. Jaya
B.P.T,M.P.T (sports)
Frequently
Asked Questions
At Physio Flex Physiotherapy, we understand that patients often have questions about treatments, recovery time, and therapy techniques. Our team is here to guide you through each step. Whether you’re curious about how long a session lasts, what to wear, or which therapy suits your condition best, we’re happy to help. Feel free to reach out or visit us in Ghaziabad for personalized answers and expert advice.

01. What conditions can physiotherapy treat?
02. How many sessions will I need?
03. Is physiotherapy painful?
04. Do I need a doctor’s referral for physiotherapy?
Why Choose Us
Experience and Expertise
Orthopedic Analysis
Recovery Focused
Medically Certified
What Our Patients Say
Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Best Physio clinic in crossing republic town .. highly recommendedPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Best physio in ghaziabadPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Highly recommend .. suffering from knee pain with in 15 session m absolutely fine .ty dr preksha ..Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Suffering from back pain since 10 days with in 10 session pain was absolutely gone ..best physio in ghaziabadPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Best physio service in GhaziabadPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. I was struggling with severe pain in my upper and lower back and couldn’t even sit for half an hour straight. After taking 10 sessions of physiotherapy here, I feel completely relieved and pain-free. The diagnosis was accurate, and the physiotherapists are highly knowledgeable and professional. Their treatment has really made a big difference in my daily life. Highly recommendedPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Best physio in ghaziabad . My elbow was fractured .with in 15 days m absolutely fibePosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. I am suffering from back pain since one months .and I am meet dr preksha after that my pain is completely gone with in 10 session ,now I am completely fine ty dr preksha nd her teamPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. i am suffering from back back pain.. i am searching many therapist but in physio flex clinic i got relief in 10 sessions. dr prelsha decided my treatment protocal like cupping , mayofaicial relaese , tens ..thank you dr preksha and her staff .. hight recommended for bone and jointPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Good physiotherapist and diagnostic skill is too good And thanks Dr.praksha And all staff is too good